Adolescence
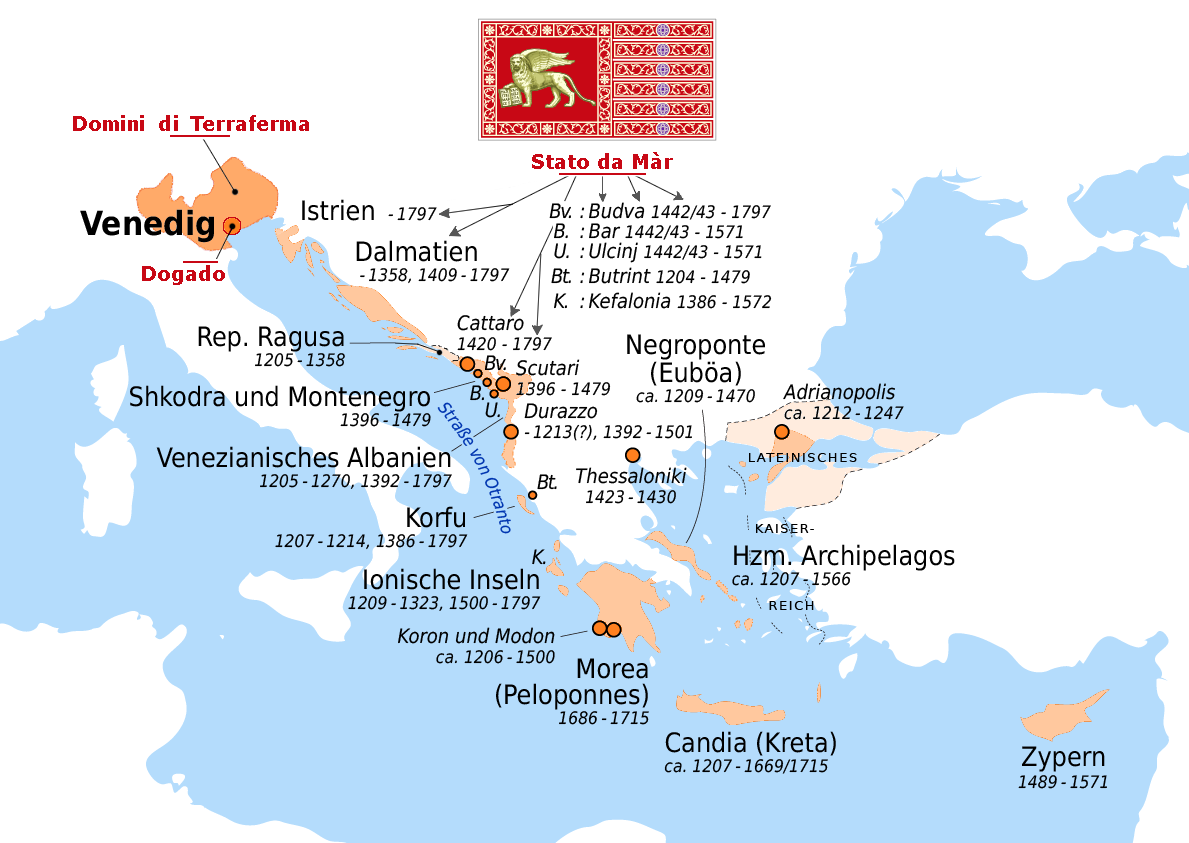

The Venetians struggled to establish their authority in Western Crete as they faced strong resistance from the locals who looked to the Greek Empire of Nicaea, one of the successor states of the Byzantine Empire for aid. By the year 1252 however the Venetians had managed to consolidate their authority. Chania was chosen as the seat of the Rector or Administrative General of the region, which was divided in separate feuda, plots of land, that were assigned to the Venetians settlers, who in return were ordered to reconstruct the city from scratch. For Venetians the island was not a temporary conquest. Their planning based on the number of soldiers -who were stationed in Chandax not Chania- their mighty navy and seemingly lax way of life of the period, pointed to people who intended to stay on the island for ever, unobstructed by serious outside threats.

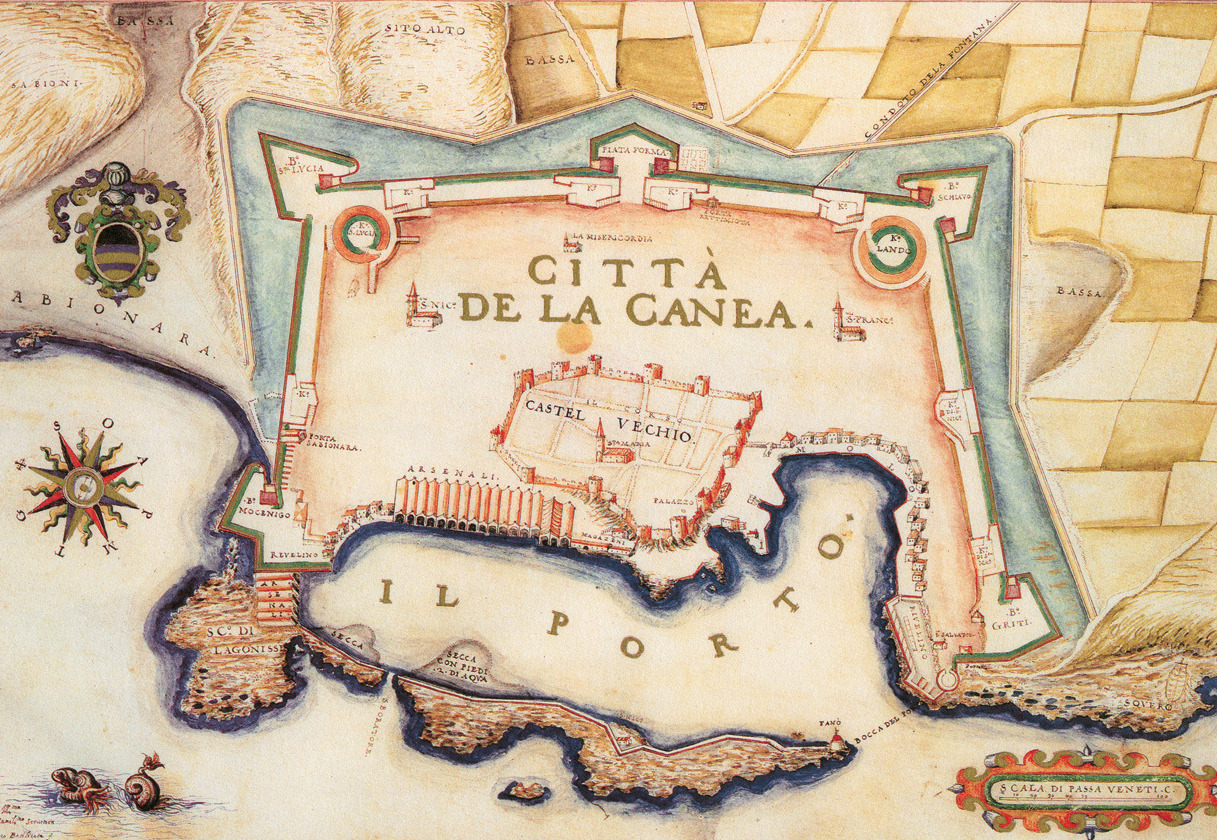
Their plans would soon have to be revised. In 1263 a fleet from Genoa sailed into Chania, defeated the Venetians soldiers and burned the city before leaving. The rebuilding of Chania would have to follow the lines of a wider, reinforced fortification that would surround all the houses around the hill of Kasteli. After 20 years of construction (1536 to 1556) the whole project was judged to be insufficient so the Venetians summoned their best engineer, Michele Sanmicheli from Verona, to build a wall that would make them feel secure enough. Strong walls which embraced the greatest part of the city, enforced with 4 bastions, towers & a protective trench strengthened the city’s defense considerably and new forts were erected on the adjacent islands of Souda, Thodorou and Gramvousa.
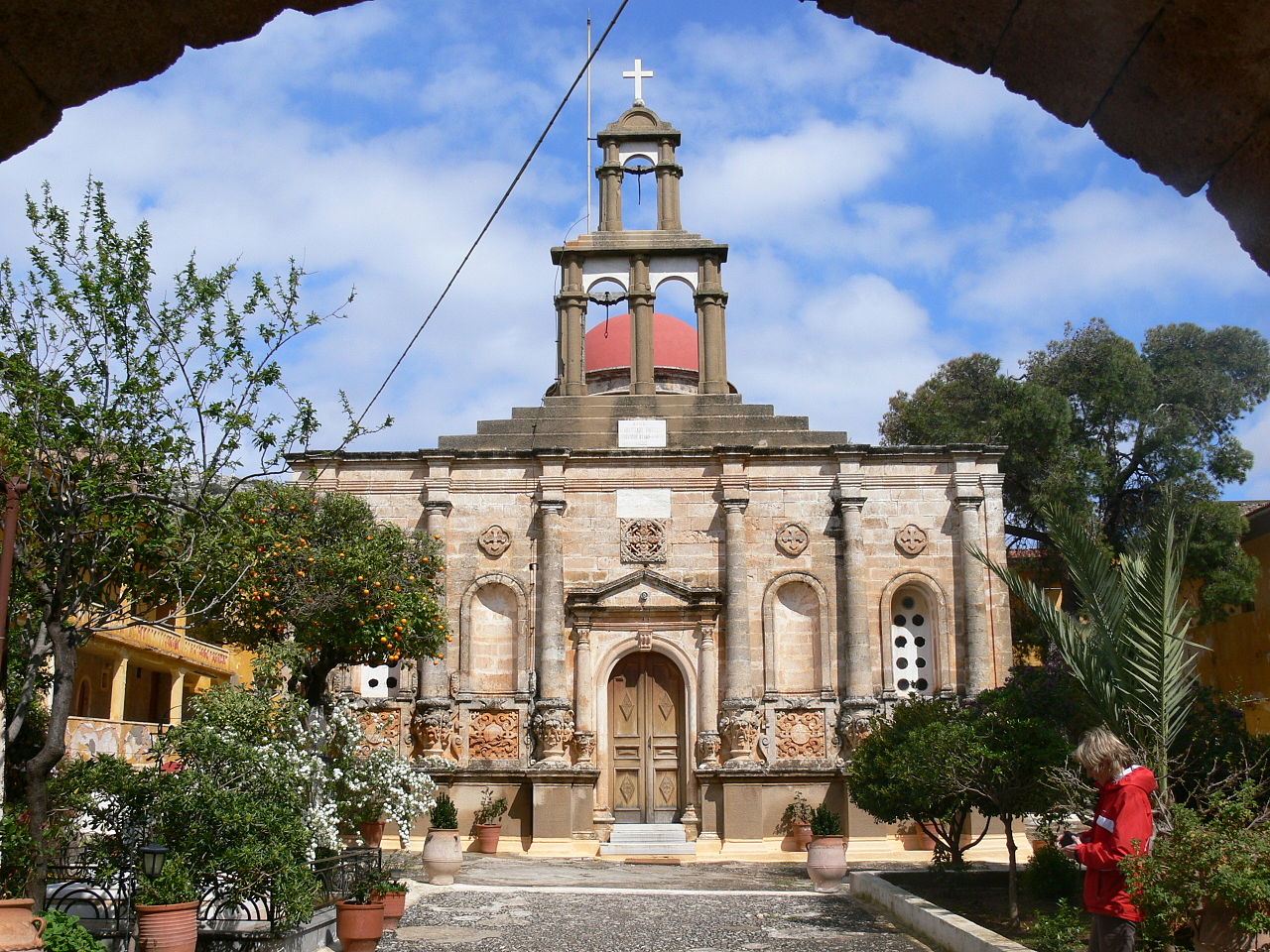

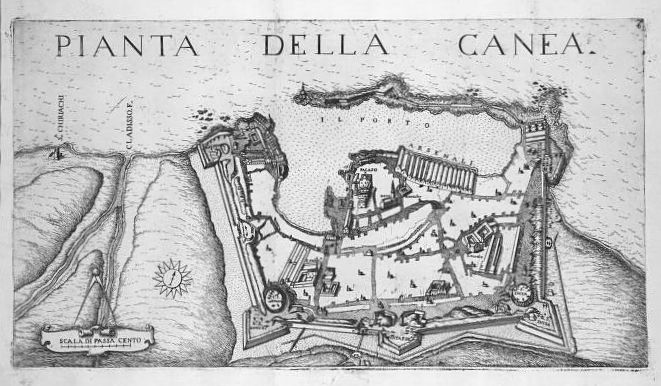

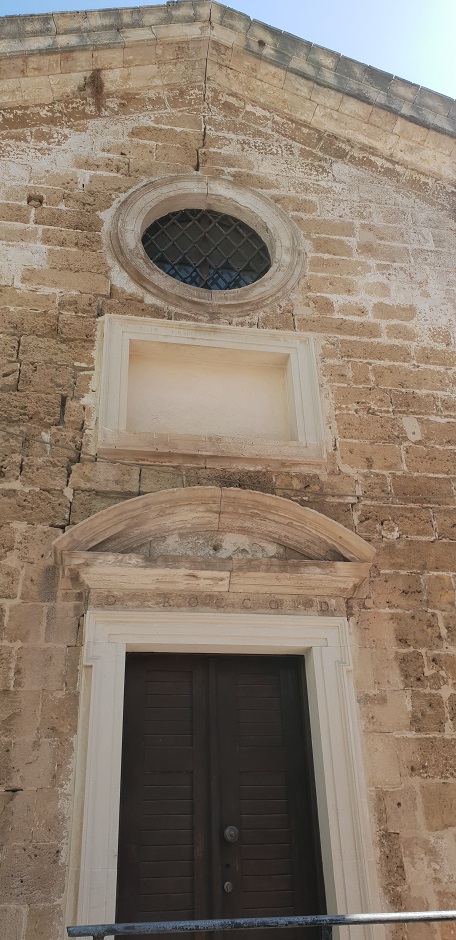
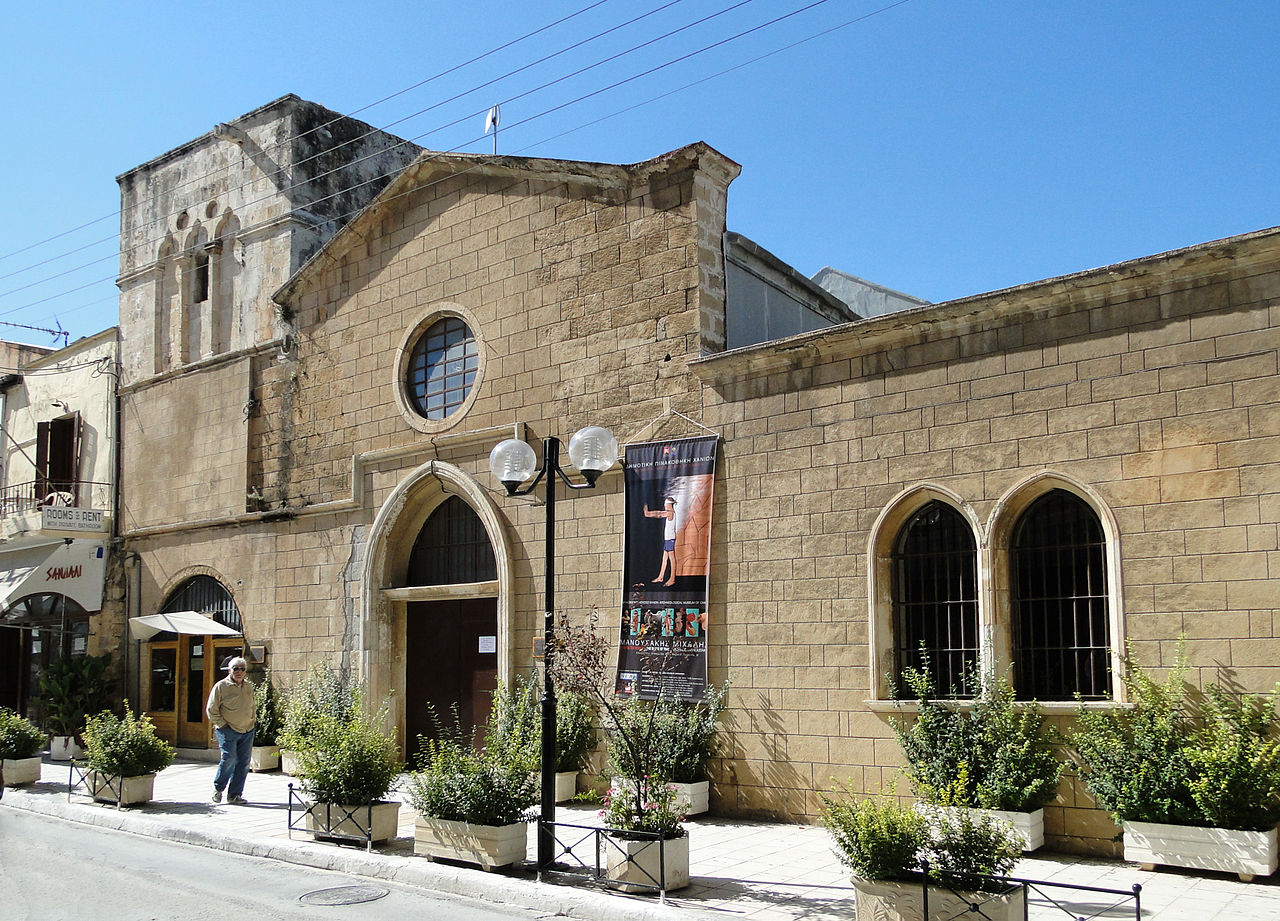
New sumptuous private & public buildings are designed & constructed such as the Palace of the Rector (governor’s palace, a hotel today) & the villas of several Venetian commanders and members of the old nobility that chose the new city on the sunbathed south for a fresh start, tall multistory houses according to the contemporary Venetian style for the new land-owners. Large Catholic churches like the Cathedral of Santa Maria dei Miracoli and Catholic convents like the Dominican Monastery of St. Francesco (old archaeological Museum at Chalidon St) are erected to cater to the needs of the Catholic population.




The local population remained faithful to their Greek-Orthodox religion and traditions. The Cretan Church continued to refer to the Byzantine Empire as the true and lawful rulers of their island up until the fall of Constantinople and even after the dissolution of the Greek Empire it kept the ties with the Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, ties that survive until this day. Most locals belonged to a cast of a second rate citizen known as villani parici, peasants that worked the fields of the Venetian rulers or the nobilitas cretensis, the feudal lords of the old aristocracy like the Skordyli or the Kallergi who very frequently led the revolts against the Latins. From 1212 until the end of the Venetian era in the mid 1660’s the Cretan population organized 27 revolutions with the Revolt of Saint Titus in 1363 uniting the colonists with the locals against the Venetian Senate.