Baby
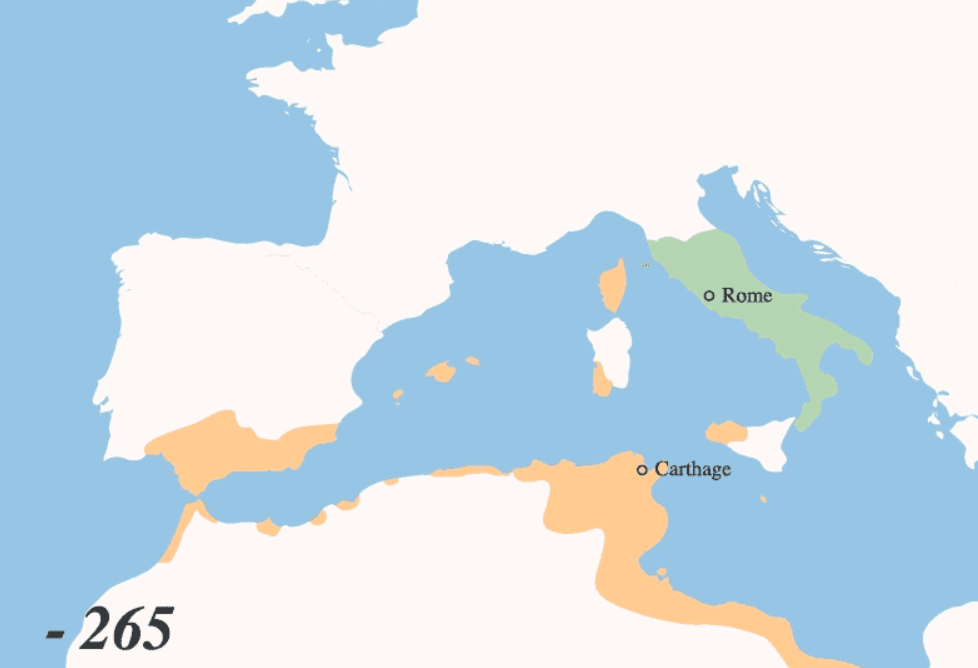
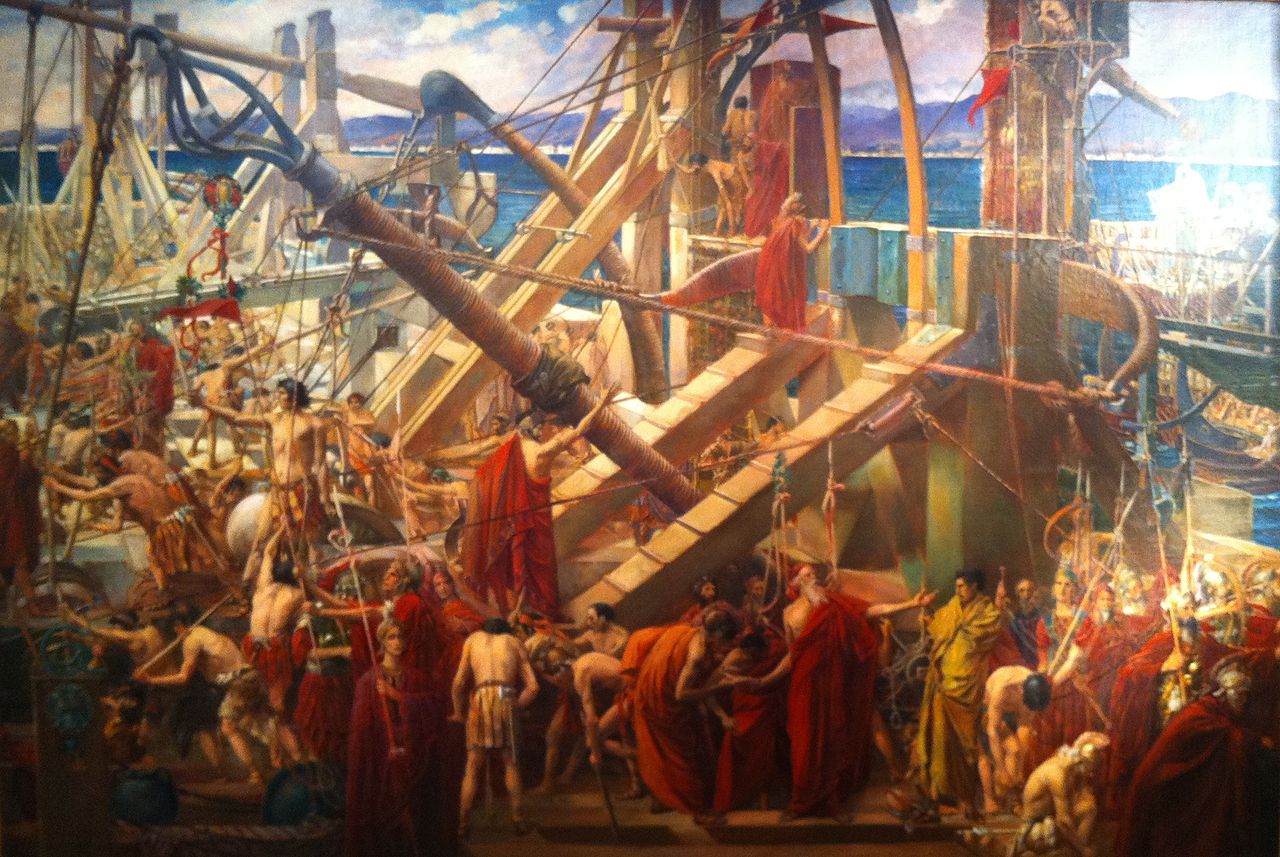
The Roman conquest of 263 BC, at the beginning of the First Punic War, opened a period of about seven centuries for Catania during which it considerably increased its importance and prestige, to the point that in the fourth century AD, Ausonio the Gallic poet and tutor of Emperor Gratian placed Catania among the first centers of the Roman Empire. Catania remained a subordinate city, subject to the payment of a share of one-tenth of the products of its territory, for almost two centuries since the administration of the province of Sicily by the proconsul Marco Valerio Levino around 210 BC. The last Greek stronghold that hadn’t yet been subdued by the Romans in Sicily, the powerful city-state of Syracuse fell after a two year siege in 212 BC.


A decisive improvement in Catania’s condition was recorded when, fifteen years after having defeated Sextus Pompeius on the island, in 21 BC Augustus raised it to the rank of a Roman colony, perhaps at the suggestion of his main collaborator Marcus Agrippa, a large landowner in the area. The imperial decision led to an increase in the number of inhabitants of Catania determined by the introduction into the city of a large body of veterans. It also led to a significant expansion of the territory of the city thanks to the acquisition of the fertile plain south of the River Simeto, previously controlled by the city of Leontini. All this, added to the various privileges associated with the colonial status, favored the economic growth of Catania during the imperial era.
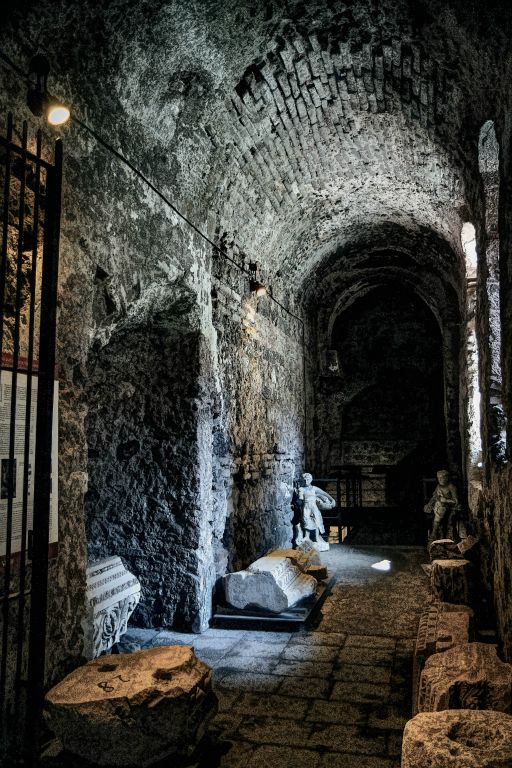
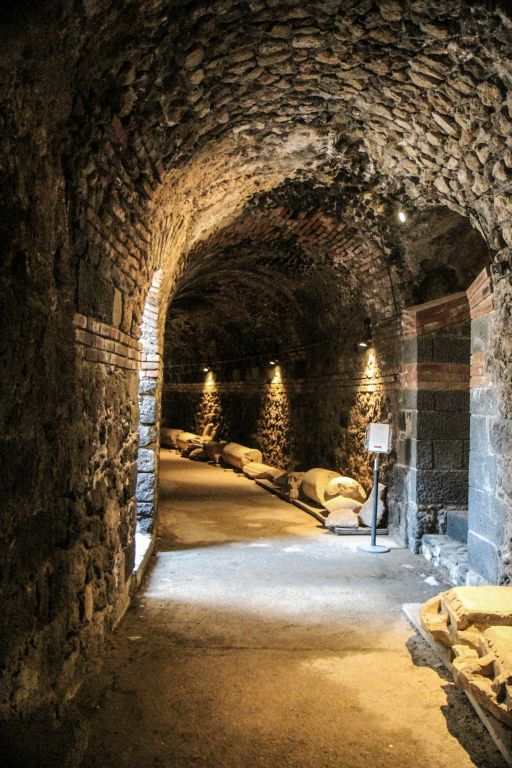



Immediately to the years of the establishment of the colony, when it was necessary to give a Roman imprint to the city, the area around the current S. Pantaleone courtyard (Roman Forum) was rearranged accordingly. Moreover, a decisive action to rearrange the city’s road network seems to date from the same period. On the basis of recent excavations conducted in via Crociferi and a manuscript map of the sixteenth century, the road network of the colony is in some way traceable to the modern one in the area that revolves around via Vittorio Emanuele in the stretch between Piazza Duomo and via Plebiscito. In the centuries of the empire, however, the Augustan city layout provided the guidelines for the expansion of the urban area, in particular towards the south, where the circus for chariot races was also built. The northern limit of the imperial city was represented by the amphitheater: built in the 2nd century AD, the building in its grandeur can be considered the crowning jewel of the whole accumulation of wealth which began in Catania with the elevation to the rank of colony. Furthermore, considered together with the other entertainment venues in the city such as the theater and the odeon, the numerous bath complexes or the highly efficient water supply system, it is all evidence of the high level of quality of life that had been achieved in Catania during the imperial age.
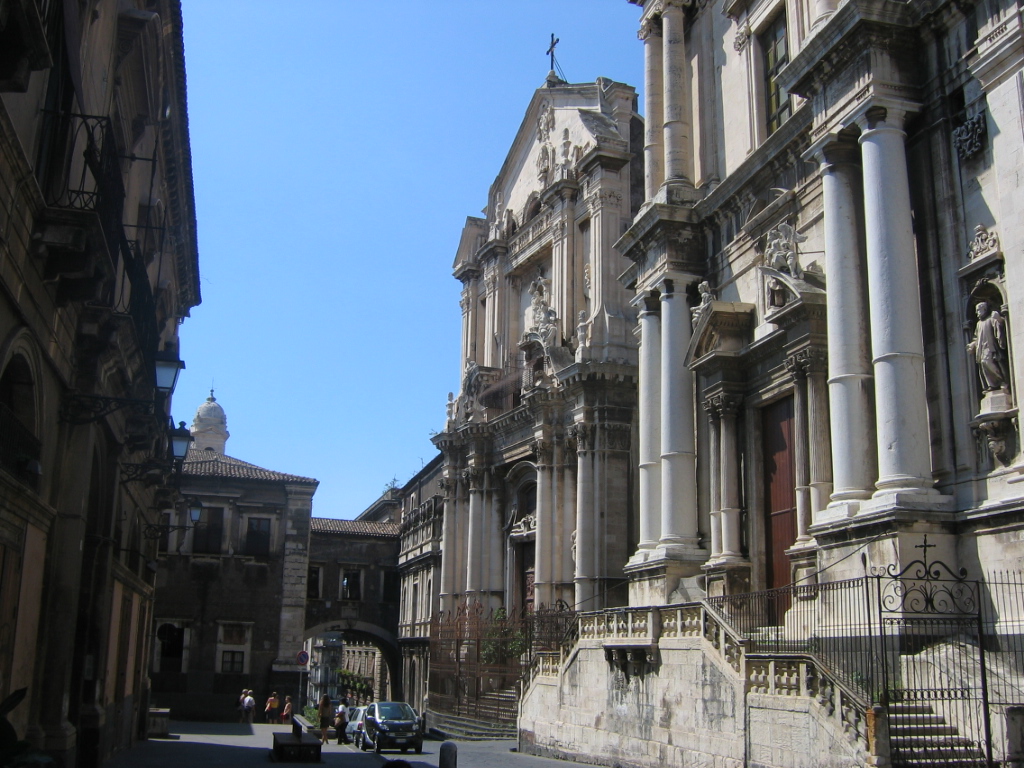
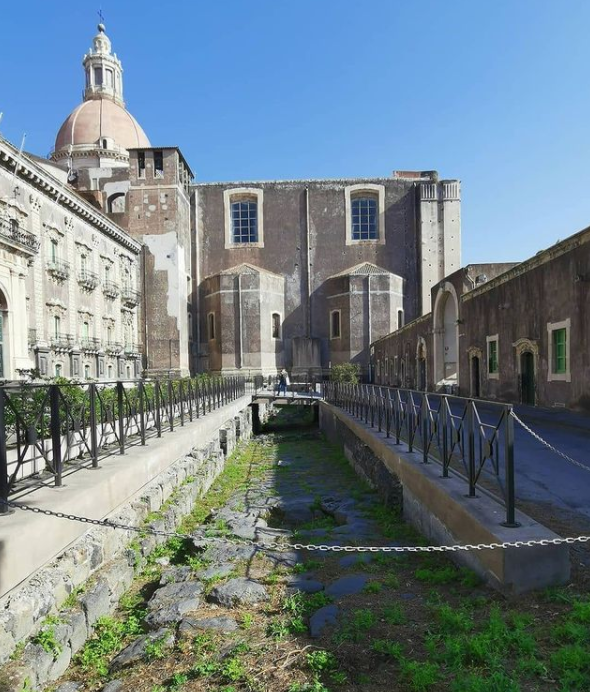


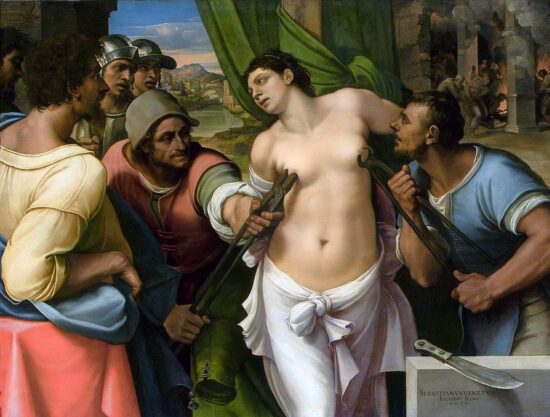
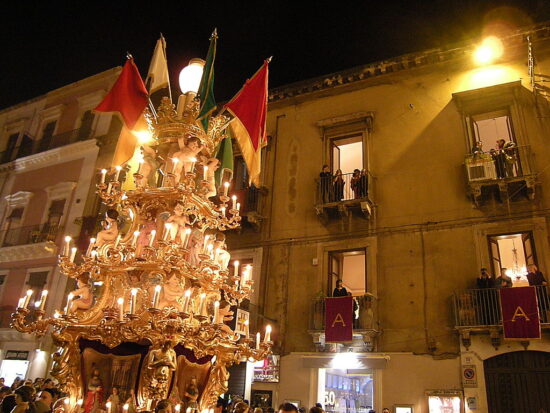
It is not possible at the moment to define exactly the times and methods of the introduction of Christianity in Catania, even if it is possible to think that here too not a few were the faithful of the new religion in the mid-third century AD when, during the persecution of emperor Decius, tradition dates the martyrdom of Agatha, the patron saint of the city. According to the legend, Saint Agatha was a beautiful 15 year old virgin from a rich and noble family of the city that had embraced the new faith. The young maiden decided to reject the courtship of the Roman prefect Quintianus and keep her vows so the prefect reported Agatha to the authorities and Agatha became one of the first and most venerated martyrs in Christian antiquity. More certain information on Christian Catania, on the other hand, is available from the 4th century AD thanks to a substantial group of inscriptions and excavations conducted in sacred or cemeterial areas.



